Introducing Incidence of TB per 100,000 population
The first indicator we would like to introduce is the incidence of tuberculosis (TB) per 100,000 people that is available from the World Health Organisations (WHO) Global TB Report. The WHO defines this indicator as:
the estimated number of new and relapse tuberculosis cases arising in a given year, expressed as a rate per 100,000 population. All forms of TB are included, including cases in people living with HIV.
This information is important to the public health community, because it reflects changes to both TB transmission and TB disease expression in the population. The distinction between these two processes is significant since you may acquire TB infection but may experience TB disease only until much later. Globally, TB incidence is falling at about 2% per year and between 2015 and 2020 the cumulative reduction was 11%. This was over half way to the End TB Strategy milestone of 20% reduction between 2015 and 2020. An estimated 66 million lives were saved through TB diagnosis and treatment between 2000 and 2020. The various methods used to estimate incidence of TB disease, based on data availability and quality at a national level, are detailed in annual WHO reports.
Latest Status in EAC, ECOWAS and SADC
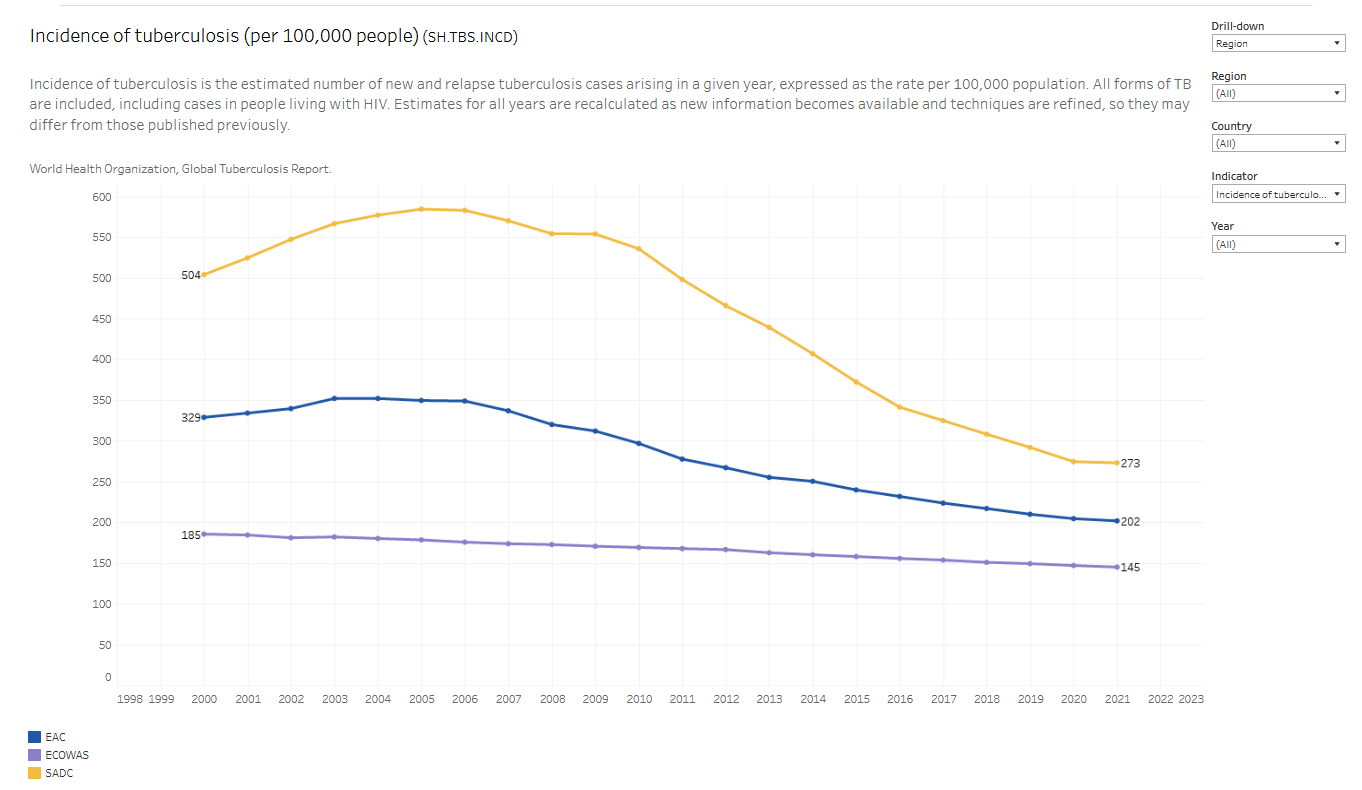
Incidence of TB per 100,000 Population for EAC, ECOWAS and SADC (Sub-Saharan Africa)
This graph shows that the highest proportion of TB incidence occurred in the SADC as compared to Eastern and Western Africa regions. SADC countries also have the highest HIV incidence in Sub-Saharan Africa. Peak incidence was observed between 2000 and 2008, with steady decline to date.
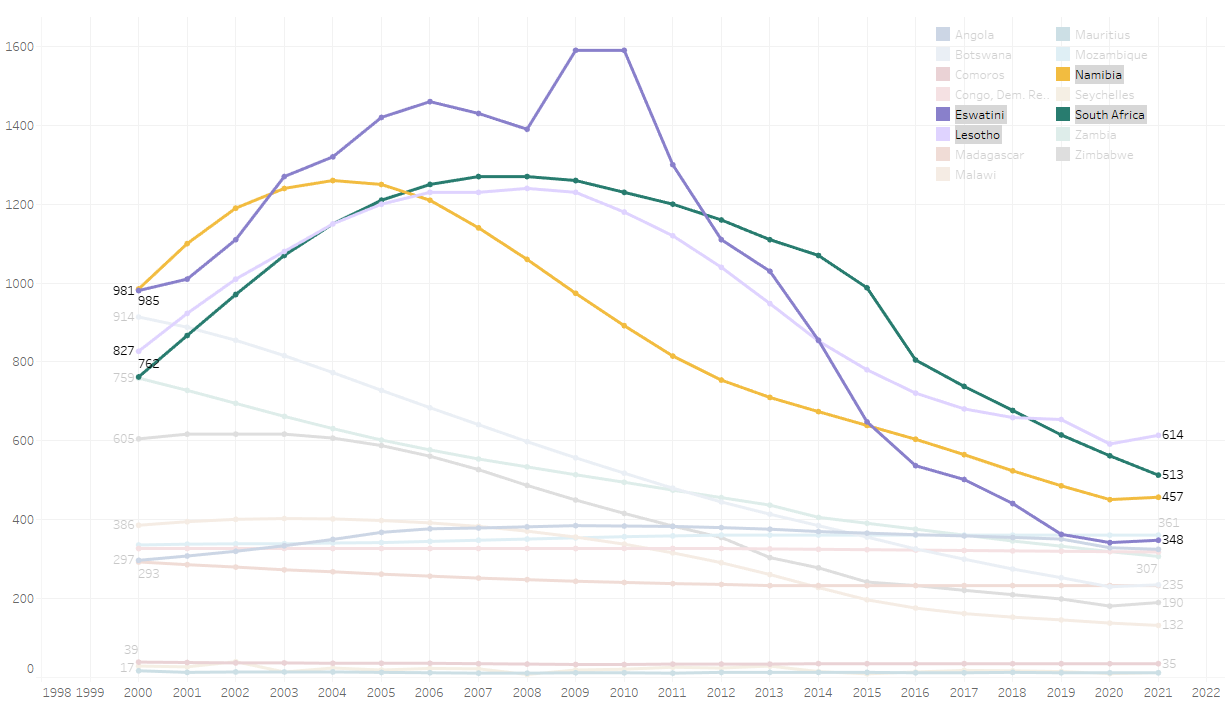
Incidence of TB per 100,000 Population in the SADC Region
The curves of Eswatini, Lesotho, Namibia and South Africa are immediately identifiable for their dramatic trajectories of new TB cases as compared to other countries in the region.
Contributing factors to declining incidence are political will and policy intent; improved point-of-care testing methods enabling faster diagnostic turnaround times; a slew of health system improvements backed by appropriately trained and skilled health workforce and, not least of all, dedicated program funding.
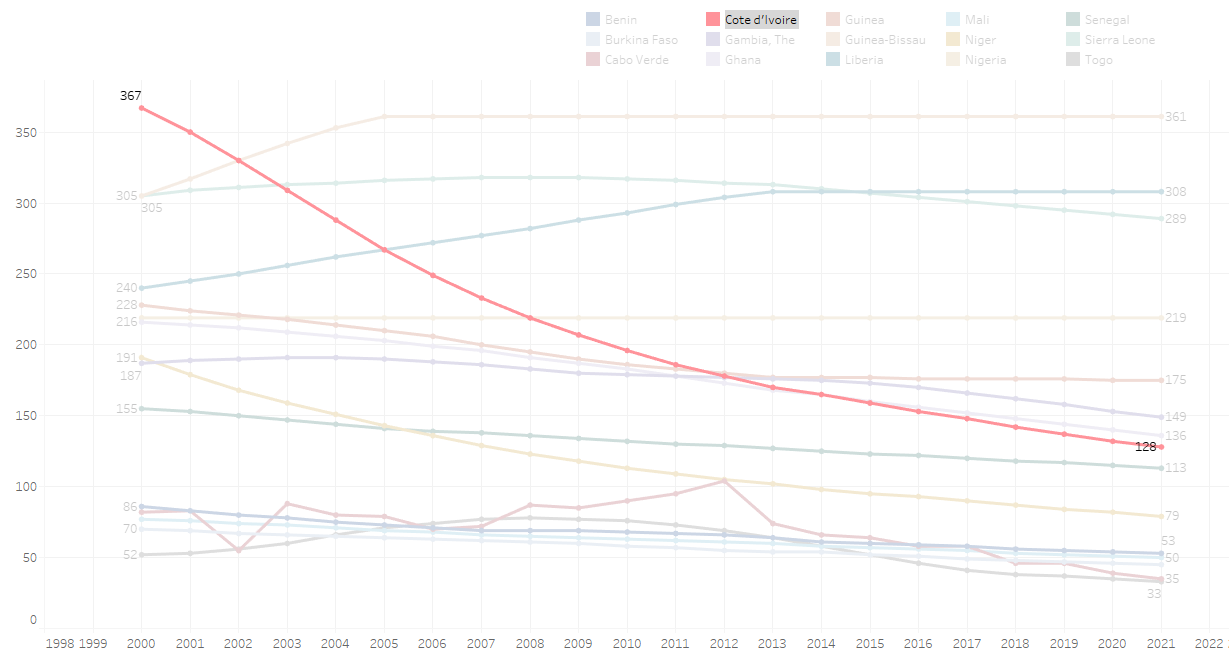
Incidence of TB per 100,000 Population in the ECOWAS Region
There is a noticeable variation in TB incidence across countries in this region. the country with the most impressive curve is Ivory Coast.
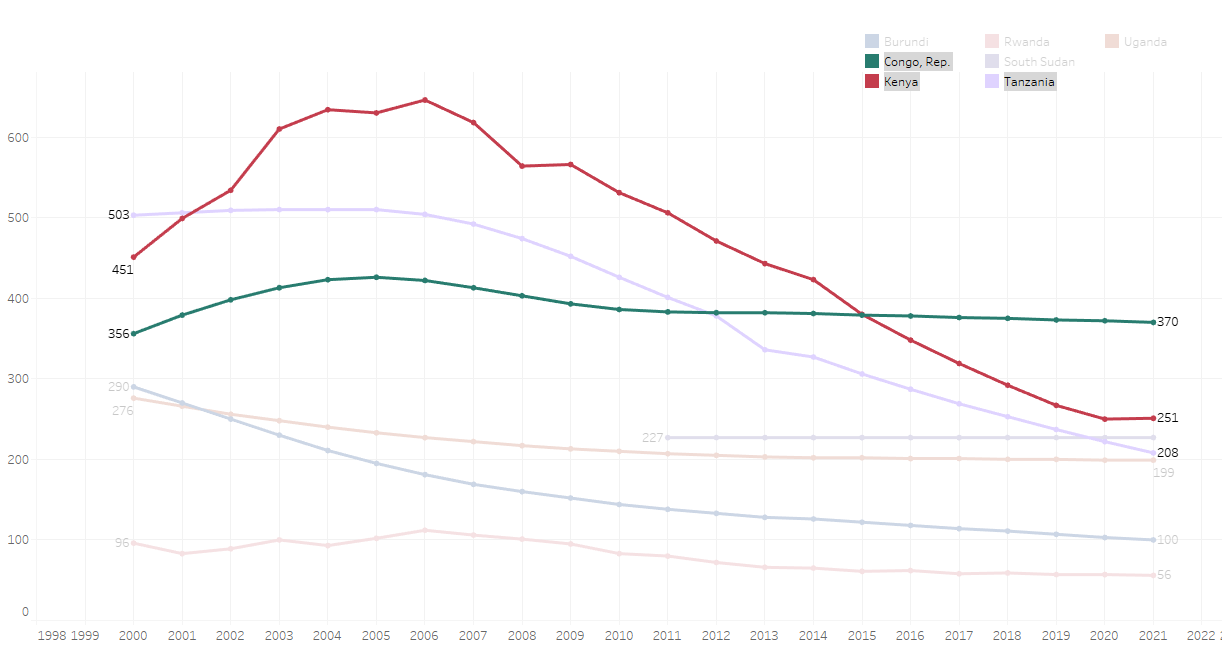
Incidence of TB per 100,000 Population in the EAC Region
Kenya and Tanzania are clear outliers in the East Africa region however the real concern is the ongoing (and unacceptably high) TB incidence in the Rep of Congo.
Live version
The interactive version is available on Tableau Public. See the guides for interacting with the dashboard, and downloading the data for World Bank DataBank on the project site.
This is part of the Armchair TB Project. Find out more about the project, and related content here.